A) the strongest hydrogen lines of any spectral type.
B) spectra of complex molecules.
C) very few spectral lines.
D) very intense spectral lines all across the spectrum.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spectral classification of a star into the lettered categories, O, B, A, F, G, K, and M is carried out by
A) finding the wavelength of peak emission in the continuum spectrum of the star.
B) determining the relative mass of the star by the study of binary star motions, in order to place it into its proper mass classification.
C) determining the total energy emitted at all wavelengths by the star, taking account of the full spread of wavelengths and their distances, in order to place the star into its luminosity class.
D) examining the relative amounts of absorption caused by various neutral and ionized atoms in a stellar spectrum.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these stars (each of which is listed with its apparent magnitude) looks brightest when viewed from Earth?
A) tau Ceti; m = +3.49
B) alpha Centauri B; m = +1.34
C) Barnard's star; m = +9.53
D) 61 Cygni A; m = +5.21
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The radial velocity curve of a star in a binary star system is a plot against time of the
A) speed of the star in a direction perpendicular to the line of sight to the star.
B) position of the star in celestial coordinates.
C) variation of Doppler shift of the star's spectral lines and hence of its speed toward or away from Earth.
D) temperature of the star as determined from the movement of the peak wavelength of its spectrum.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
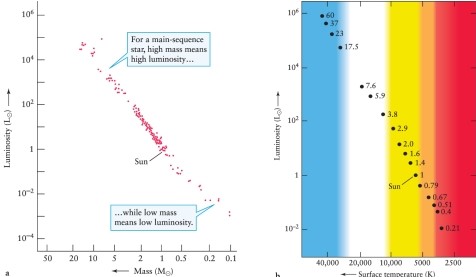
Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (Figure 12-7) and the mass-luminosity relation (Figure 12-15) in the text, to estimate the mass of Vega, an AO V main-sequence star with a surface temperature of about 10,000 K. 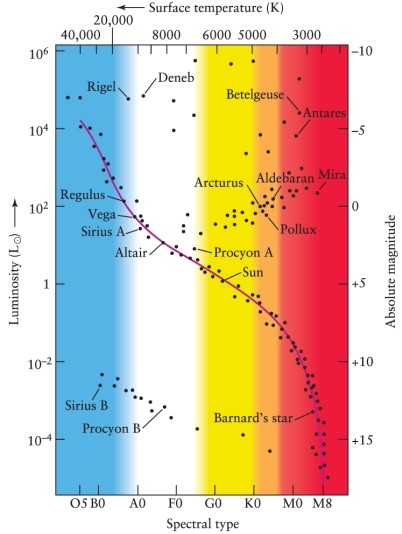
A) between 1.5 and 5.0 solar masses
B) about 10 solar masses
C) less than 1.0 solar mass
D) between 5.0 and 10.0 solar masses
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these sequences of stellar spectral classifications is in the correct order of INCREASING temperature?
A) K, M, G, F, A, B, O
B) A, B, F, G, K, M, O
C) M, K, G, F, A, B, O
D) O, B, A, F, G, K, M
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By what standard technique did astronomers in the 1930s originally determine the luminosity class (I, II, III, IV, or V) of a star?
A) combining the apparent magnitude with the measured distance to the star
B) observing the diameter of the star on a photographic plate or CCD image
C) timing how long it takes for the star to be eclipsed by a companion in an eclipsing binary star system
D) studying the absorption lines in the star's spectrum
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What observations of a star are necessary to determine the absolute magnitude of a star?
A) distance and temperature
B) apparent magnitude and temperature
C) just apparent magnitude since absolute magnitude is simply apparent magnitude + 5
D) apparent magnitude and distance
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As one moves upward and to the left on the H-R diagram, the stars become
A) cooler and redder.
B) hotter and redder.
C) cooler and bluer.
D) hotter and bluer.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chemical makeup of the Sun's surface can be determined by
A) taking a sample of the star's surface with a space probe.
B) examining the chemicals present in a meteorite because it is part of the solar system.
C) measuring the components of the solar wind with Earth-orbiting spacecraft.
D) solar spectroscopy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these four spectral classifications signifies the coolest stellar surface temperature?
A) B
B) K
C) G
D) A
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The star Phoenicis has an apparent magnitude of +3.4 and an absolute magnitude of -4.6. The North Star (Polaris) has an apparent magnitude of +2.0 and an absolute magnitude of -4.6. Assuming that no light has been absorbed or scattered by interstellar dust, one can say for sure that Polaris is
A) the same distance as Phoenicis from Earth.
B) closer to Earth than Phoenicis.
C) farther away from Earth than Phoenicis.
D) fainter than Phoenicis in the Earth's sky.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which important stellar parameter can be derived from the study of binary stars mutually bound to each other by gravitational forces?
A) stellar masses
B) distances of the stars from Earth
C) ages of the stars
D) surface temperatures of the stars
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An astronomer is observing a binary system with two stars of masses M1 and M2. She determines a, the semimajor axis (also the average distance between the stars) and P, the period of their motion. Using this information in Kepler's third law she can calculate
A) M1 or M2 but not both.
B) M1/M2.
C) M1 + M2.
D) both M1 and M2.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these types of main-sequence stars would have the LARGEST mass?
A) M
B) A
C) O
D) G
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The star Spica is classified as B1 V, which means that it is a
A) hot main-sequence star.
B) cool giant.
C) hot supergiant.
D) cool main-sequence star.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these stars (each of which is listed with its apparent magnitude) would NOT be visible to the unaided eye on a clear night?
A) tau Ceti; m = +3.49
B) alpha Centauri B; m = +1.34
C) Barnard's star; m = +9.53
D) 61 Cygni A; m = +5.21
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular star appears fainter seen through a blue filter than seen through a yellow filter. Which of these surface temperatures is possible for this star?
A) 12,500 K
B) 38,000 K
C) 8800 K
D) 3800 K
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What fraction of the stars surrounding the Sun are main-sequence stars?
A) almost all, about 90%
B) There are no main-sequence stars close to the Sun.
C) roughly half, about 55%
D) very few, about 20%
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Sun's luminosity is 3.83 *1026 watts. By the time this energy reaches Earth, it has spread out so that it provides only 1370 watts to each square meter. The orbit of Mars has a mean radius of 1.53 au. How many watts of the Sun's luminosity are provided to each square meter of the surface of Mars?
A) 34
B) 153
C) 585
D) 1578
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 254
Related Exams