A) marginal private benefit
B) marginal external cost
C) marginal social cost
D) marginal social benefit
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pollution occurs when timber is produced. If the timber market is unregulated, there will be
A) underproduction of timber compared to the efficient amount.
B) overproduction of timber compared to the efficient amount.
C) sometimes overproduction and sometimes underproduction of timber compared to the efficient amount.
D) an external benefit to producing timber.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When producers are hard to monitor and marginal costs differ across producers, _______ are an effective method to achieve efficient use of a _______.
A) individual transferable quotas; common resource
B) individual transferable quotas; excludable good
C) marginal private benefits; public good
D) individual transferable quotas; public good
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
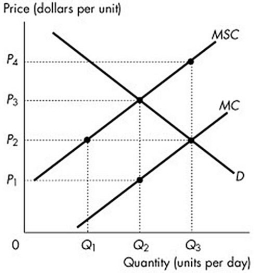 -The figure above shows the private marginal cost curve, the social marginal cost curve and the market demand curve. If a constant per unit tax is imposed that generates an efficient allocation of resources, then producers receive a per unit price of
-The figure above shows the private marginal cost curve, the social marginal cost curve and the market demand curve. If a constant per unit tax is imposed that generates an efficient allocation of resources, then producers receive a per unit price of
A) P4.
B) P1.
C) P2.
D) P3.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the production of a good creates an external cost, one method of achieving the efficient allocation is to impose a tax such that
A) MC + tax = MSC.
B) MB + tax = MSC.
C) MB - tax = MSB.
D) MC - tax = MSB.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal cost of production that is borne by the entire society is the
A) marginal private cost.
B) marginal external cost.
C) marginal social cost.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an external cost exists, who bears it in an unregulated, competitive market transaction?
A) The federal government
B) Someone other than the producers
C) The buyers of the product
D) Nobody
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the production of a good has an external cost, the
A) equilibrium quantity in an unregulated, competitive market has a marginal social cost less than the marginal social benefit.
B) equilibrium quantity in an unregulated, competitive market has a marginal social cost greater than the marginal social benefit.
C) marginal social cost curve lies below the marginal private cost curve.
D) marginal social benefit curve lies above the marginal private benefit curve.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the production of some industrial good that involves air pollution. The table below gives the marginal social cost (MSC) , the marginal cost (MC) , and the marginal social benefit (MSB) for each level of output (Q) . 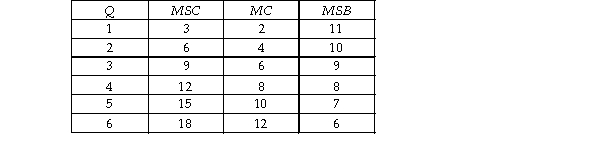 To arrive at the efficient market equilibrium the government could impose a tax of
To arrive at the efficient market equilibrium the government could impose a tax of
A) $9.
B) $8.
C) $3.
D) $4.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Coase theorem, part of what is needed for private transactions to be efficient is that property rights
A) need to be defined by the government to avoid producers exploiting high transactions costs.
B) must be defined, and it is crucial as to who owns the property.
C) need not be defined as long as there are no transactions costs present.
D) must be defined, but it does not matter who owns the property.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _______ is the cost of production paid by the producer plus any cost paid by everyone else when another unit of a good or service is produced.
A) marginal social cost.
B) marginal external cost.
C) marginal private cost.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
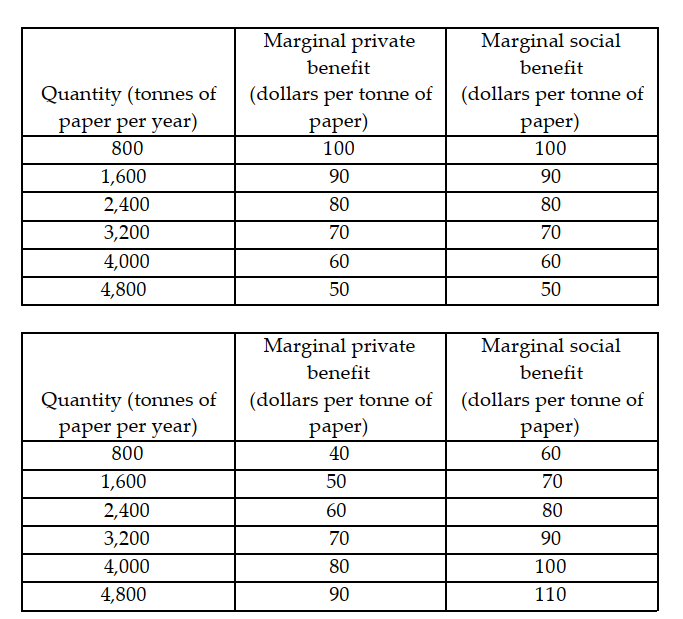 -The tables above show the marginal costs and benefits from the production of paper. If the market is perfectly competitive and unregulated, the
-The tables above show the marginal costs and benefits from the production of paper. If the market is perfectly competitive and unregulated, the
A) allocation of resources is efficient.
B) market equilibrium produces 800 tonnes less than the efficient amount.
C) market equilibrium produces 800 tonnes more than the efficient amount.
D) market equilibrium produces 1,600 tonnes more than the efficient amount.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -The figure above shows the private marginal cost curve, the social marginal cost curve and the market demand curve. If the market is unregulated, then the price is
-The figure above shows the private marginal cost curve, the social marginal cost curve and the market demand curve. If the market is unregulated, then the price is
A) P1.
B) P3.
C) P4.
D) P2.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generating electricity creates air pollution. This industry, if left unregulated will produce at an inefficient market equilibrium where
A) marginal social cost equals marginal private cost.
B) marginal private cost equals marginal social benefit.
C) marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit.
D) marginal social benefit is greater than marginal social cost.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
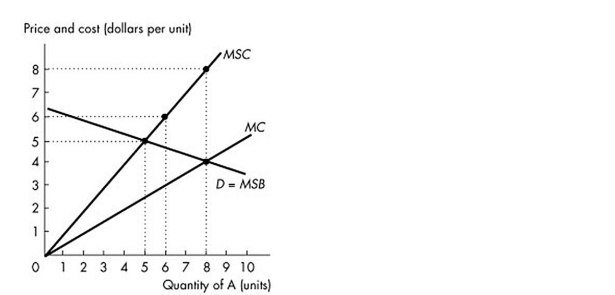 -The figure above shows the demand curve, the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A. What is the efficient quantity of good A?
-The figure above shows the demand curve, the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A. What is the efficient quantity of good A?
A) 6 units
B) 0 units
C) 8 units
D) 5 units
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When producing a good creates pollution, an external cost, and the government imposes a tax equal to the marginal external cost, then
A) transaction costs will be high.
B) the efficient amount of the good will be produced.
C) the amount of output moves farther away from the efficient amount.
D) property rights must have already been established.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let MC be the marginal private cost per megawatt hour (MWh) of producing electricity using coal. Let MSC be the marginal social cost per MWh and T be the tax per MWh. To achieve efficiency, the tax should be set so that
A) MSC = MC + T.
B) MC + MSC = T.
C) MC = T.
D) MC = MSC + T.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government assigns private property rights to a common resource, then the
A) marginal private cost becomes equal to the marginal social cost.
B) resource is underutilised.
C) government needs to set a quota to achieve efficiency.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) MSC = MC + Marginal external cost
B) MSC = Marginal external cost + marginal external benefit
C) MC = Marginal external cost - MSC
D) MC = Marginal external benefit + MSC
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
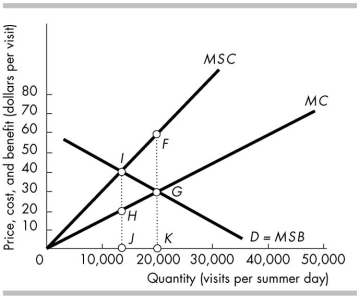 -The figure above illustrates the problem of overcrowding and external costs experienced during the summer months in a national park. If the market is unregulated, in equilibrium the external cost of visiting the national park is given by the distance between
-The figure above illustrates the problem of overcrowding and external costs experienced during the summer months in a national park. If the market is unregulated, in equilibrium the external cost of visiting the national park is given by the distance between
A) points F and G.
B) points H and G.
C) points I and F.
D) points G and K.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 152
Related Exams