A) nuclear magnetic resonance
B) x-ray crystallography
C) treatment with mercaptoethanol
D) treatment with detergents
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lipid molecules possess a different fundamental structural make-up from the others?
A) Fatty acids
B) Cholesterol
C) Triglycerides
D) Sphingolipids
E) Glycolipids
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true?
A) Receptors are often invaginated into the cell after binding to their specific molecule.
B) A given receptor type is present at a constant level on the outside of a cell
C) In certain disease states, the level of a given receptor is increased or decreased
D) Binding of receptors to ligands sometimes shows hyperbolic binding curves
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does amphipathic mean?
A) having both positive and negative charges
B) having both acid and base properties
C) having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
D) having two stereoisomers
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What characteristic is most used to define lipids?
A) ionic charge
B) melting point
C) solubility
D) ability to bind metal ions
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The order-disorder transition (melting) in membranes
A) is cooperative
B) can be monitored by fluorescence techniques
C) can be monitored by spin labeling
D) all of these
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The key reaction of eyesight (in dim light) involving vitamin A is:
A) Reaction of the protein complex called Rhodopsin.
B) A cis-trans isomerization of a double bond.
C) Bleaching of a pigment in the retina.
D) Reaction of Rhodopsin and cis-trans isomerization of a double bond.
E) All of these.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Passive transport is the same as:
A) simple diffusion
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) primary active transport
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning active transport is true?
A) It takes place in the same direction as a concentration gradient.
B) It requires no expenditure of energy by the cell.
C) It can be compared to water running downhill.
D) A membrane-associate protein must be involved.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aspirin produces most of its analgesic effects by
A) binding to the plasma membrane of nerve cells
B) inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin A
C) inhibiting the synthesis of phospholipids
D) inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Plants need cholesterol in their membranes to counteract the rigidity of the cell wall.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following methods of transport across a membrane does not require a protein?
A) Passive transport
B) Facilitated transport
C) Active Transport
D) Simple diffusion
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With what compound are fatty acids reacted to make a fat or oil?
A) cholesterol
B) glycerol
C) sphinganine
D) ceramide
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 8A 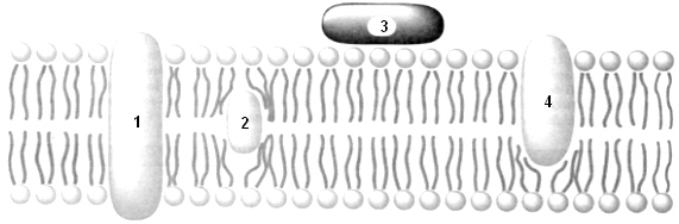 Refer to Exhibit 8A.Protein #2 would most likely function as a:
Refer to Exhibit 8A.Protein #2 would most likely function as a:
A) Carrier
B) Channel
C) Cell identity
D) Receptor
E) You cannot tell from the diagram.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) All fatty acids have an even number of carbons
B) Most fatty acids have an odd number of carbons
C) Fatty acids are equally likely to have an even number of carbons as they are an odd number
D) Fatty acids with an odd number of carbons are more rare than those with an even number
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following four fatty acids has the lowest melting point? 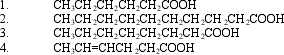
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major difficulty in extracting receptor proteins from membranes is that
A) it is difficult to remove the proteins from the membrane without denaturation
B) there may be very few molecules of the protein in a cell
C) receptor proteins tend to have high molecular weights
D) all of these
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does cholesterol affect membrane fluidity?
A) It tends to increase the fluidity.
B) It tends to decrease the fluidity.
C) It doesn't have any specific effect on fluidity.
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true?
A) Fatty acids with trans double bonds may be particularly unhealthy because they increase the ratio of LDLs to HDLs.
B) A fatty acid with 14 carbons and one trans double bond will behave more like a saturated fatty acid with 14 carbons than will an unsaturated fatty acid with a cis double bond.
C) Fatty acids with trans double bonds can be formed by hydrogenation reaction of polyunssaturated fatty acids
D) fatty acids with trans double bonds tend to have higher melting points than those with cis double bonds all else being equal
E) All of these are correct
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following lipid vitamin is often used to preserve foods from spoiling:
A) A
B) D
C) E
D) K
E) None of these preserves food.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 90
Related Exams